
Scientific Name
Plukenetia Volubilis
Color
Vibrant yellow colored oil
Production Areas
In the highlands of Peru
Grade
Organic
Form
Powder and Gel Capsules

Scientific Name
Plukenetia Volubilis
Color
Vibrant yellow colored oil
Production Areas
In the highlands of Peru
Grade
Organic
Form
Powder and Gel Capsules
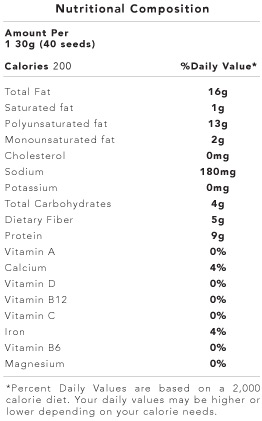
Facts
Sacha Inchi, also known as the Inca peanut, is the seed of a plant that grows in the highlands of Peru. Despite being a fairly recent discovery in the health community of the United States, sacha inchi has been cultivated and used as a food source for 3,000 years in the Amazon rainforest. The fruit that these seeds grow in is inedible, but when lightly roasted with low heat the seeds take on a crisp nutty flavor.
Nutrients
Sacha Inchi is much more than just a pleasant snack food. These seeds are rich in protein, omega-3, -6, and -9, alpha tocopherol vitamin E, carotenoids (vitamin A), and fiber. This superfood is easily digested and unlikely to cause allergies or irritation. The oil is also available. It has a similar flavor to olive oil, just slightly lighter and nuttier, but it contains more protein and omega-3.
Preliminary Health Research
Vegans and vegetarians should look into omega-3 rich foods to supply this essential nutrient. There are very few plant foods that supply a decent amount. Sacha inchi now joins purslane, chia seeds, flaxseed, and microalgae as vegan omega-3 superfoods and another way to sneak healthier essential fats into your life. The studies are still underway at this time, but sacha inchi is showing promise in many areas.
1. Cholesterol – Sacha Inchi lowers LDL and raises HDL cholesterol. Cholesterol levels may not be the biggest marker for cardiovascular problems we once thought them to be, but they are still a concern and can reflect dietary problems and genetic dispositions toward some diseases.
2. Well Being – These seeds contain a good amount of tryptophan, a precursor for serotonin. Serotonin is a feel-good hormone and neurotransmitter that helps us deal with stress and feel calm and happy. The omega 3 also reduces inflammation in the brain, which can cause mood shifts, headaches, and more.
3. Weight Loss – Higher serotonin levels, thanks to the tryptophan, also regulate appetite so we don’t get cravings, overeat, or snack more than we need to.
4. Brain Health – The majority of our brain is composed of fat. We need good, healthy fats to resupply those cells and to continually fight inflammation. Inflammation in the brain can cause depression, fatigue, memory issues, and exaggerated responses to pain.
5. Heart Health – Sacha Inchi improves circulation while lowering blood pressure, cholesterol, and inflammation throughout the body. All of this makes for a healthier, happier, less stressed cardiovascular system, from arteries to heart and beyond.
6. Diabetes – Omega-3 helps control glucose levels. Many doctors and researchers argue that omega-3 may actually reduce insulin resistance in those with type 2 diabetes. Omega-3 also lowers triglyceride levels, which are often high in diabetics.
7. Bone Health – Omega-3s helps the body absorb calcium. Foods rich in omega-3 improve bone density, staving off some of the deterioration that occurs as we age.
8. Vision – The vitamin E, vitamin A, and omegas in Sacha Inchi can improve vision and maintain eye health. Like the brain, the eyes rely on a good amount of fat, and are prone to inflammatory damage, especially as we get older.
9. Joint Health – The anti-inflammatory nature of Sacha Inchi may make it a good supplement to ease joint pain and rheumatoid arthritis. Consider combining Sacha Inchi oil with ginger for even more benefits.
10. Skin and Hair – Omega 3 fatty acids are vital to healthy hair and skin. They help us regulate oil production, keep skin elastic, lock in hydration, protect against sun damage, and help repair damage when it occurs.
Advantages
Sacha Inchi contains two very important essential fatty acids (also known as polyunsaturated fats): alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an omega-3 fatty acid and linoleic acid (LA), an omega-6 fatty acid. The human body is incapable of producing these fatty acids. They must be consumed from our diet. Both types offer health benefits.
Studies link omega-3s to a wide range of health improvements including maintaining a healthy heart and circulatory system, retaining healthy joints, and lowering triglyceride levels. Studies are still underway to show the effectiveness of omega-3s on maintaining healthy mental function. Omega-6 fatty acids have been linked to anti-inflammatory properties.
Medical research suggests that a higher intake of omega−6 fatty acids in comparison to the intake of omega-3 fatty acids may increase the likelihood of a number of diseases. While there is no set optimal ration, scientific agreement shows that individuals should consume more omega-3 fatty acids, and less omega-6 fatty acids.
Use
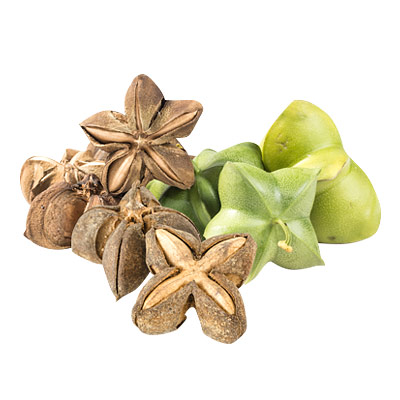
Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia volubilis linneo) is a perennial vine that is indigenous to the Peruvian Amazon Forest. Growing up to 2 meters, it produces small, green, star-shaped pods. Plants are said to have a long production time, with some producing year after year for decades. There have been plants found that have been producing for 75 years. The production time is also increased due to harvests throughout the year.
The pods are inedible fruit. Generally the pods are left to dry on the vine before being harvested. The seeds are then harvested from the pods after the fruit has dried. The raw seeds must be lightly roasted with low heat before being consumed. While also known as Inca Peanuts, Mountain Nuts or Inca Nuts, they are actually seeds and not nuts.
Cold-pressed from these seeds is an extremely rich, high quality and nutritious oil. The pulp is a by-product used commonly for soap, bread, flour, feed for fish and cattle and in the cosmetics industry.
The Sacha Inchi seed has a high oil content – more than 50%. The oil is extracted by simple cold pressing and does not require refining. The introduction of high heat to the process of making the oils can degrade the flavor, nutritional value, and color.
The oil can be used for spreading over salads, or lightly seasoning vegetables. It can also be used to make delicious marinades. It is similar to olive oil, but with a lighter taste. The oil is not suitable for cooking as heat destroys the omega-3.
The seeds can be eaten as a snack, or added them to your favorite recipes.