
Scientific Name
Chenopodium quinoa
Color
White, Red, Black or Tricolor
Production Areas
Santa Cruz, Bolivia
Grade
Organic or Conventional

Scientific Name
Chenopodium quinoa
Color
White, Red, Black or Tricolor
Production Areas
Santa Cruz, Bolivia
Grade
Organic or Conventional
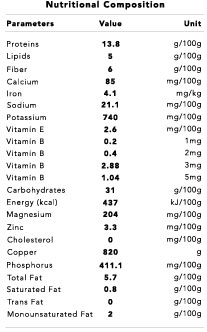
Facts
Quinoa is a pseudo-grain belonging to the family of Chenopodaceas. Also known as the Golden Grain of the Andes, quinoa was domesticated and used in the diet of Tiwanaku and Inca civilizations for over 5000 years. There are over 17 varieties of quinoa growing in northern Ecuador to southern Bolivia. The most demanded variety in the world is the Royal Quinoa which grows only in Southern Altiplano of Bolivia because it is perfectly adapted to its extreme characteristics: a cool, dry weather high (between 200 and 400 mm annual rainfall), saline soils and altitudes (between 3700 and 4200 m above sea level). These conditions allow producing a larger grain with specific organoleptic characteristics and higher nutritional value.
Nutrients
Protein, carbohydrate, thiamin (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin, vitamin C, calcium, iron, phosphorus.
Preliminary Health Research
Quinoa is one of the few plant foods that are nutritionally complete, having the right balance of proteins, carbohydrates and minerals, necessary for human life.
This food is produced by a plant of great strength to suit various terms of latitude and altitude up to 4000 meters, and can grow in arid and semiarid regions.
The scientific name is Chenopodium Quinoa Wild, and between its denominations, it has also had the name of "Inca wheat". A website on "Quinoa" states that according to some research this food became part of the diet of humans in the Andean region at least 5,000 years before Christ.
Advantages
Contains amino acids, improve immune function, promotes the formation of antibodies and cellular repair. Improves intestinal transit, contains lots of fiber. It is rich in protein and calcium, even more than corn and rice, helps prevent decalcification and osteoporosis.
Contains starch, which provides energy. Helps to delay metastases (cancer).
Use
Quinoa can be combined with legumes such as dried beans, beans and lupine to improve the quality of the diet; swelled cereals, extruded, flaked, grated and hot cereals. Almost all of the flour industry products are prepared with whole grains and quinoa flour.
The whole plant is used as forage. Crop residues are also used to feed cattle, sheep, pigs, horses and poultry.
The leaves, stems, and grains have medicinal uses, including working as an anti-inflammatory, an analgesic against toothache, and a disinfectant for the urinary pathways; they are also used in case of fractures, in internal bleeding and as an insect repellent.